コンプリート! in absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow with about 677359-In absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow with about
Without enzyme, biological reaction essential to life takes 23 billion years All biological reactions within human cells depend on enzymes Their power as catalysts enables biological reactions Given the large number of biological reactions that require enzymes, it seems that there might be an advantage to reactions that are slow in the absence of a catalyst, and that indeed seems to be the case If the uncatalyzed reaction is very slow, an organism can control when the reaction happens by providing an enzyme at the desired timeSpecialized class of protein molecules Enzymes act as catalysts, to increase the rates of chemical reactions, but they do not cause a reaction to occur that would not proceed spontaneously without the enzyme The reactions of metabolism would occur at extremely slow rates at normal body temperature and pH in the absence of enzymes

Dr Hunter Cell Biology Bioenergetics Enzymes And Metabolism
In absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow with about
In absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow with about- Experimental methods used to observe very slow reactions can generate important information for drug design "Enzymes that do a prodigious job of catalysis are, handsdown, the most sensitive "Now we've found a reaction that – again, in the absence of an enzyme – is almost 30 times slower than that," Wolfenden said "Its halflife – the time it takes for half the substance to be consumed – is 23 billion years, about half the age of the Earth Enzymes can make that reaction happen in milliseconds"




Enzyme Inhibitor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
B) There are very few different enzymes but each can catalyze many different reactions C) Enzyme catalyzed reactions are the minority in biological systems because, under biological conditions, most chemical reactions are spontaneous D) There are many different enzymes known, each catalyzing one or more specific chemical reactions E) CellsENZYME KINETICS • The rate of the reaction catalyzed by enzyme E A B ↔ P is defined as ΔA or ΔB or ΔP Δt Δt Δt • A and B changes are negative because the substrates are disappearing • P change is positive because product is being formed • EnzymeBirth 8 Figure 4 shows that in the absence of an enzyme, some biological reactions are slow on a geological—or even a cosmological—timescale How did these reactions get started
Ab initio (ie in the absence of any initial nucleic acid) Ogata and Miura was very slow The synthesized DNA could not be detected until the reaction proceeded for 40 min to 1 h(, 21) In this paper, we report that if a thermophilic Restriction Enzyme (REPol Reaction)The standard reaction Study the reaction given below CO_ (2)H_ (2)O underset ("EnZyme")hArr H_ (2)CO_ (3) In absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow, with 0 molecules of H_ (2)CO_ (3) being formed in an hour In presence of enzyme the reaction speeds up dramatically with about 6000,000 molecules formed every second The mechanism for the enzymecatalyzed reaction would consist of at least two steps, the first step being formation of the enzymesubstrate (ES) complex, which is an intermediate If the formation of the ES complex is thermodynamically favorable, it would be represented on a reaction coordinate diagram at a lower level along the energy axis
Experiment 10 – Enzymes Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts for biological reactions Enzymes, like all catalysts, speed up reactions without being used up themselves They do this by lowering the activation energy of a reaction All biochemical reactions are catalyzed by enzymesB are about twelve enzymes, at least one responsible for each step in the metabolic pathway c may not be any enzymes involved if this is a natural cell product d is one enzyme that carries this process through to the end product e is one enzyme for degradation and another enzymeChapter 14 Question Suppose that a certain biologically important reaction is quite slow at physiological temperature toward to seven Celsius in the absence off a catalyst, assuming that the collision factors remain the same Fishes, eh?




Water As The Reaction Medium In Organic Chemistry From Our Worst Enemy To Our Best Friend Chemical Science Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0scc




Enzyme Assays Sciencedirect
Absence of enzymes, the same reaction takes place relatively slowly,withahalflifethatmayspanmanyhours,days,oryears Some biological reactions may be slower still in the absence of enzymes The individual bonds connecting the components of cellulose and other polymers, readily attacked by water in theI think what you're looking for is the Arrhenius equation This link has a big, thorough treatment of activation energy and catalysis, the whole shebang of yourAbsence of carbonic anhydrase would make this reaction very slow o Enzymes speed chemical reactions by lowering activation energies and allowing reactions to achieve equilibrium more rapidly Specificity o High specificity in reactions catalyzed and the substances involved o Absolute specificity – enzyme acts only on one substance Ex




Enzyme Kinetic Report Effect Of Substrate Concentration On Studocu




Without Enzymes Biological Reaction Essential To Life Takes 2 3 Billion Years Unc Study Biochemistry And Biophysics
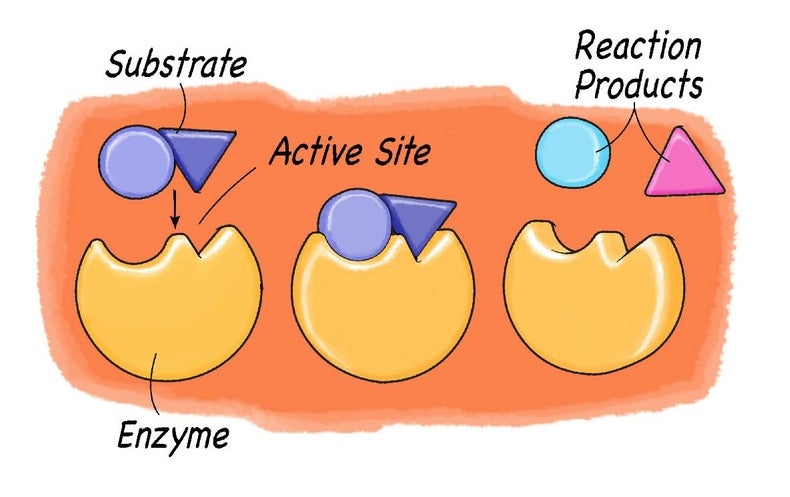
Enzyme kinetics involves the study of enzyme reactions and the factors affecting it The molecules at the beginning of the reaction are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called the productsThe basic enzyme reaction involves the binding of the enzyme to its substrate so that a chemical reaction can occur This would simply mean that when an enzymeEnzymes function as organic catalysts A catalyst is a chemical involved in, but not changed by, a chemical reaction Many enzymes function by lowering the activation energy of reactions By bringing the reactants closer together, chemical bonds may be weakened and reactions will proceed faster than without the catalystThat is, the reaction must have ΔG < 0 The reactions of metabolism would occur at extremely slow rates at normal body temperature and pH in the absence of enzymes An




In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2 Co 3 Is Very Slow With About



Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry
Enzymes (/ ˈ ɛ n z aɪ m z /) are proteins that act as biological catalysts (biocatalysts) Catalysts accelerate chemical reactionsThe molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as productsAlmost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to Relat Area MoL Biol 11,1266 The slowbinding and slow, tightbinding inhibition of enzymecatalysed reactions John F Morrison lnhibitors o f enzymecatalysed reactions can be divided into four classes according to the rate and strength of their interactions with enzymes In the absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow, with about 0 molecules of H 2 CO 3 being formed in an hour But using an carbonic anhydrase, the reaction speeds dramatically with about 600,000 molecules being formed every second The enzyme has accelerated the reaction rate by about 10 million times



Frontiers Germinal Centre Shutdown Immunology




Fitness Effects But No Temperature Mediated Balancing Selection At The Polymorphic Adh Gene Of Drosophila Melanogaster Pnas
Thus, the reaction takes place very slowly But the addition of enzymes lowers the activation energy of reaction and allows a large number of molecules to react at a time For example, In the absence of enzyme, this reaction is very slow, with about 0 molecules of H2CO3 being formed in an hourFor example, In the absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow, with about 0 molecules of H 2 CO 3 being formed in an hour However, by using the enzyme present within the cytoplasm called carbonic anhydrase, the reaction speeds dramatically with about 600,000 molecules being formed every second When enzyme catalysed reactions are observed, the rate would be vastly higher than the same but uncatalysed reaction For example CO2 H2 O →Carbonic anhydrase H2 CO3 carbon dioxide water carbonic acid In the absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow, with about 0 molecules of H2CO3 being formed in an hour




Study The Reaction Given Below Co 2 H 2 O Underset Enzyme Harr H 2 Co 3 Youtube




Reactions Enzymes
On the other hand, if biological reactions were not very slow in the absence of enzymes, then biologically important molecules would disintegrate too rapidly to be of any use to living organisms So the very existence of life can be said to depend on the difference in rate between uncatalyzed reactions and enzymecatalyzed reactionsAn enzyme completely complementary to its substrate would be a very poor enzyme Consider an imaginary reaction, the breaking of a metal stick The uncatalyzed reaction is shown in Figure 86a We will examine two imaginary enzymes to catalyze this reaction, both of which employ magnetic forces as a paradigm for the binding energy used by realWhen enzyme catalysed reactions are observed, the rate would be vastly higher than the same but uncatalysed reaction For example CO 2 H 2 O carbon dioxide water H 2 CO 3 carbonic acid In the absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow, with about 0 molecules of H 2 CO 3 being formed in an hour However, by using the enzyme present within the cytoplasm called carbonic



Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry




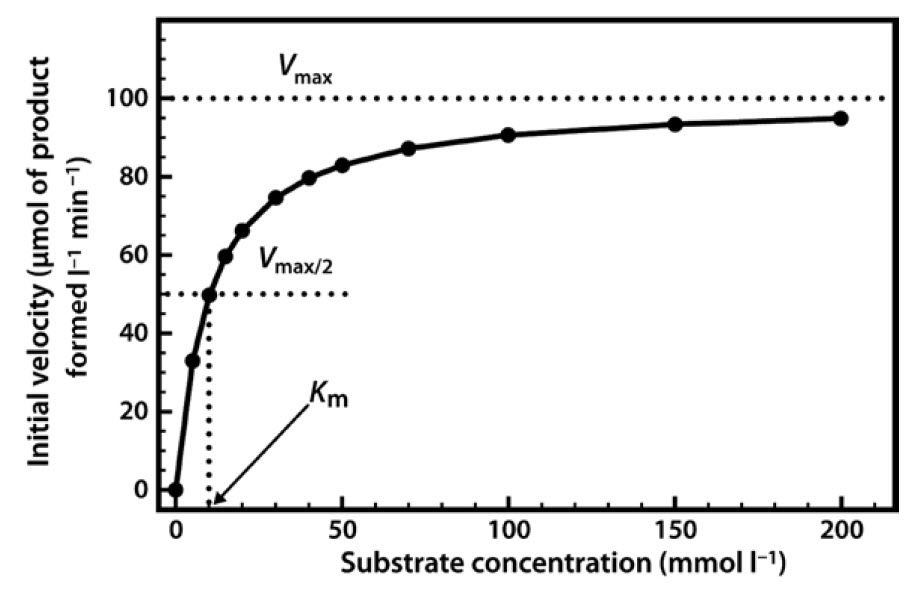
Commemorating The 1913 Michaelis Menten Paper Die Kinetik Der Invertinwirkung Three Perspectives Deichmann 14 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
Enzymes, whilst having an important role in the reaction of many chemicals within the body, are not consumed in the reaction, and so are able to catalyze many reactions in their life cycle Enzymes are able to reduce the activation energy of the reaction; Study the reaction given below In absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow, with 0 molecules of being formed in an hour In presence of enzyme the reaction speeds up dramatically with about 6000,000 molecules formed every second Name the enzyme which has accelerated up the reaction by 10 million timesIn fact, typically, an enzyme accelerates the rate of a reaction by factors of at least a million compared to the rate of the same reaction in the absence of the enzyme Most biological reactions do not occur at perceptible rates in the absence of enzymes One of the simplest biological reactions catalyzed by an enzyme is the hydration of CO2




Cu Acid The Absence Of Any Enzyme This Reaction Is Very Slow With About 000 Molecules Of Hco3 Being Formed In An Hour However By Using The Wme Present Within The Cytoplasm




Pdf Brief Review On Enzyme Activity
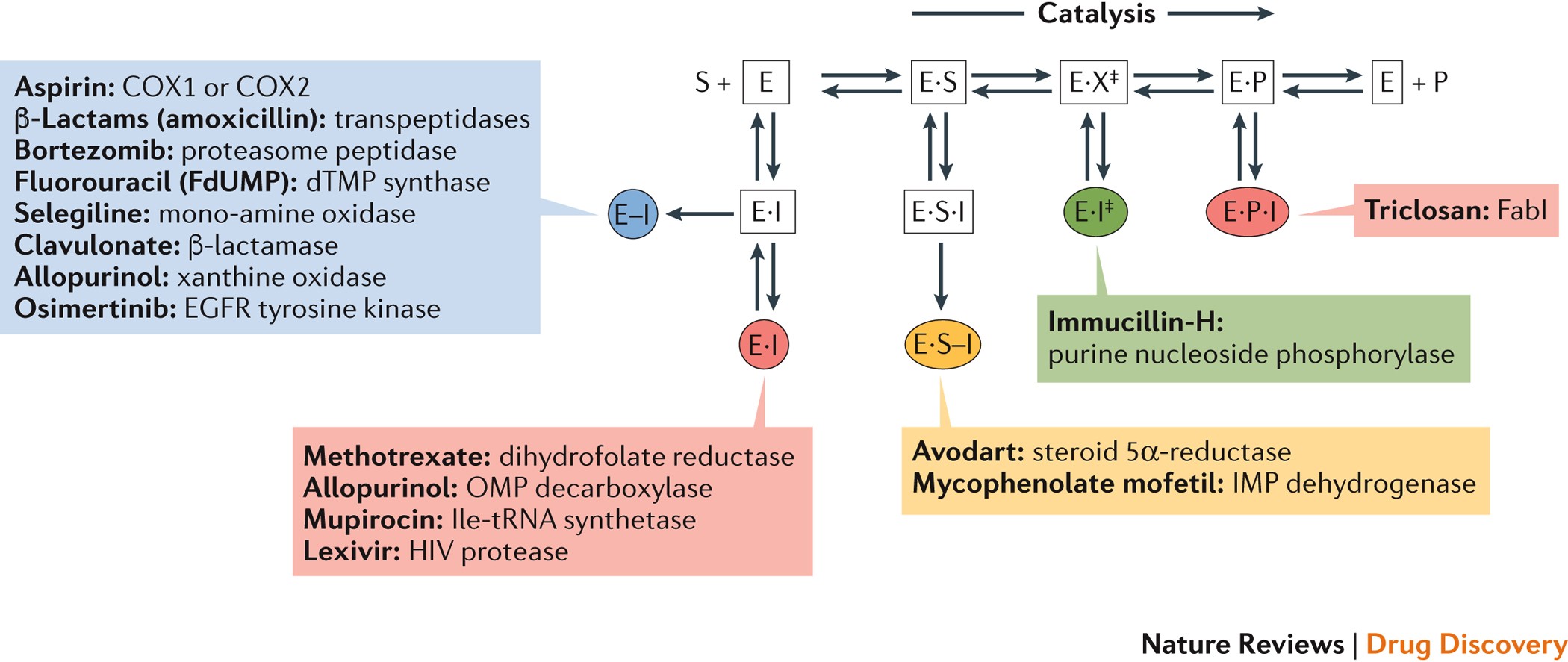
Without enzyme catalyst, slowest known biological reaction takes 1 trillion years CHAPEL HILL All biological reactions within human cells depend on enzymes Their power as catalysts enablesAnd oxygen Although the reaction is strongly favored thermodynamically, it is very slow unless catalyzed Catalase increases the uncatalyzed rate of H2O2 decomposition In the presence of catalase, the decomposition of H2O2 occurs 10 8 times faster than in the absence of catalase Indeed, enzymes may increase the rate of a reaction as much as 1017fold Reactions requiredAnswer (1 of 3) The simple answer goes like this For the enzyme mediated process shown below E S = ES → EP → E P where E is the enzyme, S is the substrate processed by the enzyme, ES is the enzymesubstrate complexand P is the product Note that the process E



Mechanistic Enzymology In Drug Discovery A Fresh Perspective Nature Reviews Drug Discovery




Looking Back A Short History Of The Discovery Of Enzymes And How They Became Powerful Chemical Tools Heckmann Chemcatchem Wiley Online Library
Once a substrate is bound, its transformation often transpires in a few milliseconds In the absence of enzymes, the same reaction takes place relatively slowly, with a halflife that may span many hours, days, or years Some biological reactions may be slower still in the absence of enzymes• In the absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow • Ie 0 molecules of H2CO3/Hour HSE Zoology Blog 8 9 • By using the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, the reaction speeds is 600,000 molecules /second • The enzyme has accelerated the reaction rate by about 10 million times HSE Zoology Blog 9 10By how much Muslim enzyme lowered the activation energy overreaction to achieve 10 to the power of five fold increase in the reactionary so less




Reactions Enzymes



Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry
10 Hysteresis (slow adaptation of the enzyme structure or conformation to new reaction conditions) The enzyme, when added to the assay mixture, may slowly adopt a more active form, due to the different pH, ionic conditions, dilution, presence of reducing agents , etc The lag or delay of the kinetics should disappear upon preincubation ofEnzymes act as catalysts to increase the rates of chemical reactions, but they do not cause a reaction to occur that would not proceed spontaneously without the enzyme; Enzyme names and classification Enzymes typically have common names (often called 'trivial names') which refer to the reaction that they catalyse, with the suffix ase (eg oxidase, dehydrogenase, carboxylase), although individual proteolytic enzymes generally have the suffix in (eg trypsin, chymotrypsin, papain) Often the trivial name also indicates the substrate on which the enzyme




Enzyme



2
This conformational transition of the free enzyme (in the absence of any chemical reaction) may be observed by following the 1 fluorescence change of the protein after a thermal perturba f6 = 111 tion and the time constant, A3, of the slowest exponential rate process may be determined 8Lism of an organism at the enzyme concentrations found in cells, but the same reactions, in the absence of enzymes, proceed vastly more slowly (Fig 1) For example, the decarboxylation of orotidine 5′phosphate (OMP), the final step in the biosynthesis of pyrimidines—and thus nucleic acids—proceeds with a halflifeClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ The enzyme carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the hydration of CO2 This reaction CO2 H2O → H2CO3 , is involved in the transfer of CO2 from tissues to the lungs via the bloodstreamOne enzyme molecule hydrates 10^6 molecules of CO2 per second How many kgs of CO2 are hydrated in one hour in one liter by 1 × 1^6M enzyme?




Enzyme Assays Sciencedirect




Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity A Level Biology Revision Notes
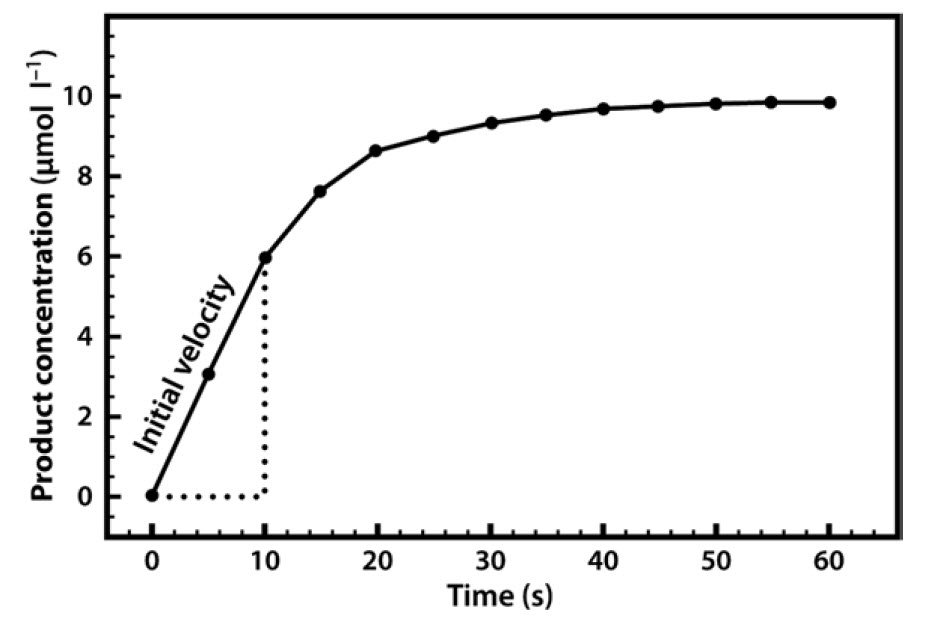
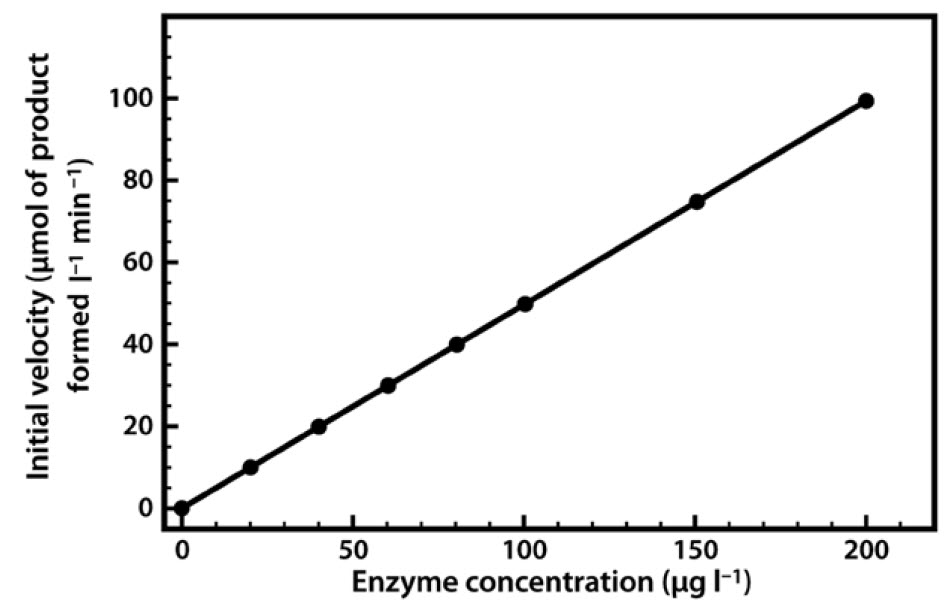
Methods In the absence of enzymes, the rate of a reaction can be thought to increase linearly with substrate concentration The reaction rate is given as dp/dt, or the change in product over time where S is the substrate concentration, and k isFor biological systems, enzymes help speed up spontaneous reactions If a chemical reaction requires an input of energy, then the for that reaction will be positive In this case, the products have more free energy than the reactants These products are essentially energystoring molecules, and their formation is through endergonic reactionsEnzymes may slow reactions relative to their previous reaction rates Enzymes accelerate reactions, but the rates of a particular enzyme's reactions may depend on inhibitors and substrate concentrations Thus they are at times malleable catalysts which may control reactions based on substrates and inhibitors



Exploring Enzymes Scientific American




Artificial Multienzyme Scaffolds Pursuing In Vitro Substrate Channeling With An Overview Of Current Progress Acs Catalysis
Figure 63 Mechanisms for slow binding inhibition of enzymatic reactions (A) The enzyme reaction in the absence of inhibitor(B) A singlestep binding mechanism for which the association rate (determined by k 3) or dissociation rate (determined by k 4) or both are inherently slow A twostep binding mechanism for which the first step is simple, rapid equilibriumThe energy required to break bonds between the reactants, and form new bonds in theQuestion Description Activity 1 Determining the Reaction Rate in the Presence or Absence of Cellobiase Data Table 1 Comparison of Reaction Cuvettes to Standard Cuvettes Time (minutes) Cuvette Standard that is Most Similar Amount of pnitrophenol (nmol) 0 START S1 8 END S1 1 E1 S2 2 E2 S3 4 S4 6 E4 S5



Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry



Enzymes
In the absence of any enzyme this reaction is very slow, with about 0 molecules of H2CO3 being formed in an hour However, in the presence of cytoplasmic enzyme carbonic anhydrase, the reaction speeds dramatically with about 600,000 molecules being formed every second The enzyme has accelerated the reaction rate by about 10 million timesSome nonenzymatic catalysts of slow reactions, including PLP as a catalyst of amino acid decarboxylation, and the Ce IV ion as a catalyst of phosphate ester hydrolysis, have been shown to meet that criterion The work reviewed here suggests that elevated temperatures collapsed the time required for early evolution on Earth, furnishing an appropriate setting for exploring the vast



Introduction To Enzymes And Their Applications Book Chapter Iopscience




Off To A Slow Start Analyzing Lag Phases And Accelerating Rates In Steady State Enzyme Kinetics Sciencedirect




In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2 Co 3 Is Very Slow With About
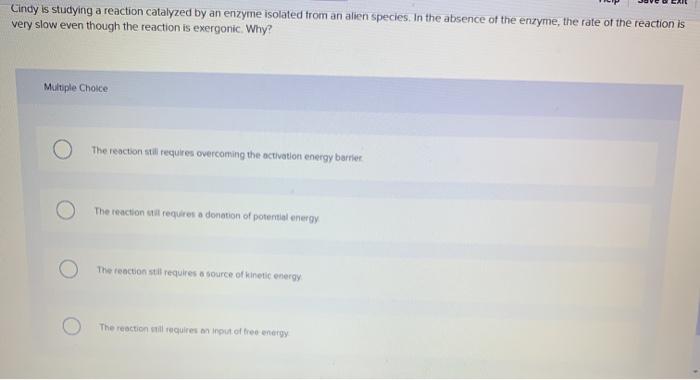



Cindy Is Studying A Reaction Catalyzed By An Enzyme Chegg Com




Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium Has Three Transketolase Enzymes Contributing To The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Journal Of Biological Chemistry




Enzyme Assays Sciencedirect
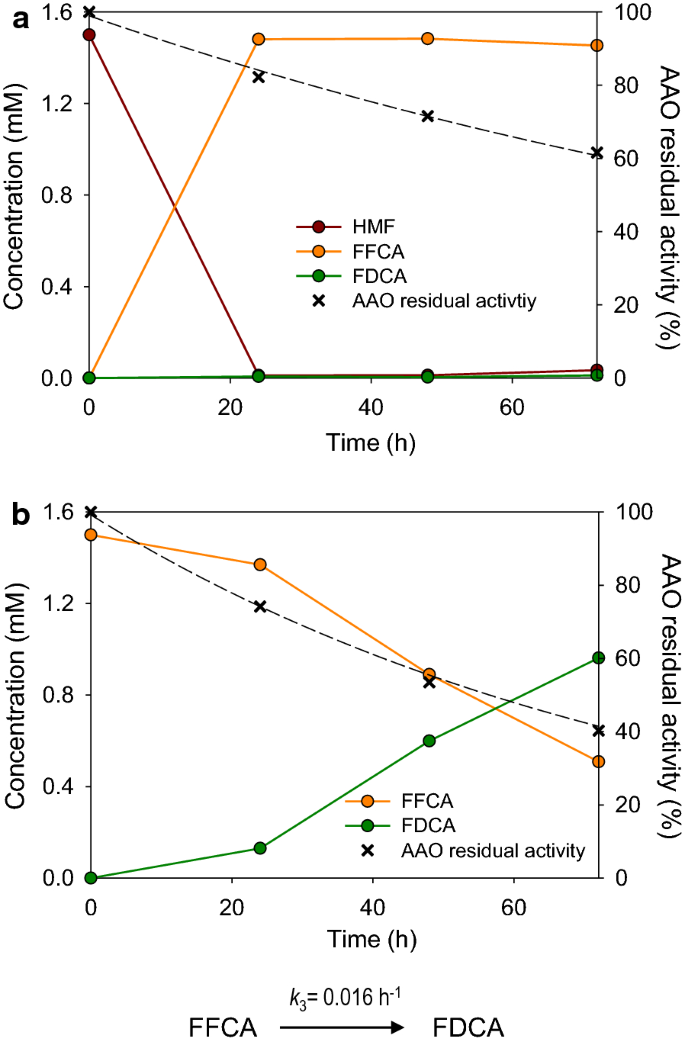



Complete Oxidation Of Hydroxymethylfurfural To Furandicarboxylic Acid By Aryl Alcohol Oxidase Biotechnology For Biofuels Full Text




Cu Acid The Absence Of Any Enzyme This Reaction Is Very Slow With About 000 Molecules Of Hco3 Being Formed In An Hour However By Using The Wme Present Within The Cytoplasm



In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2
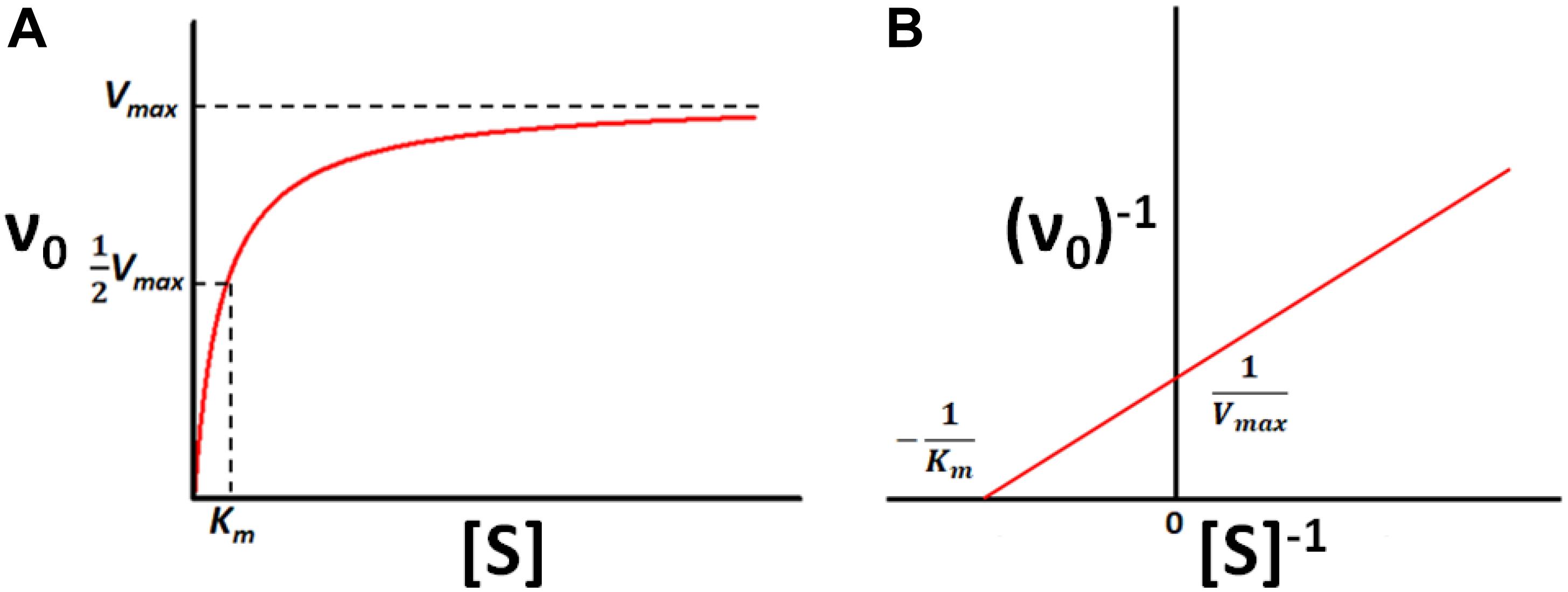



Frontiers Enzyme Kinetics By Isothermal Titration Calorimetry Allostery Inhibition And Dynamics Molecular Biosciences
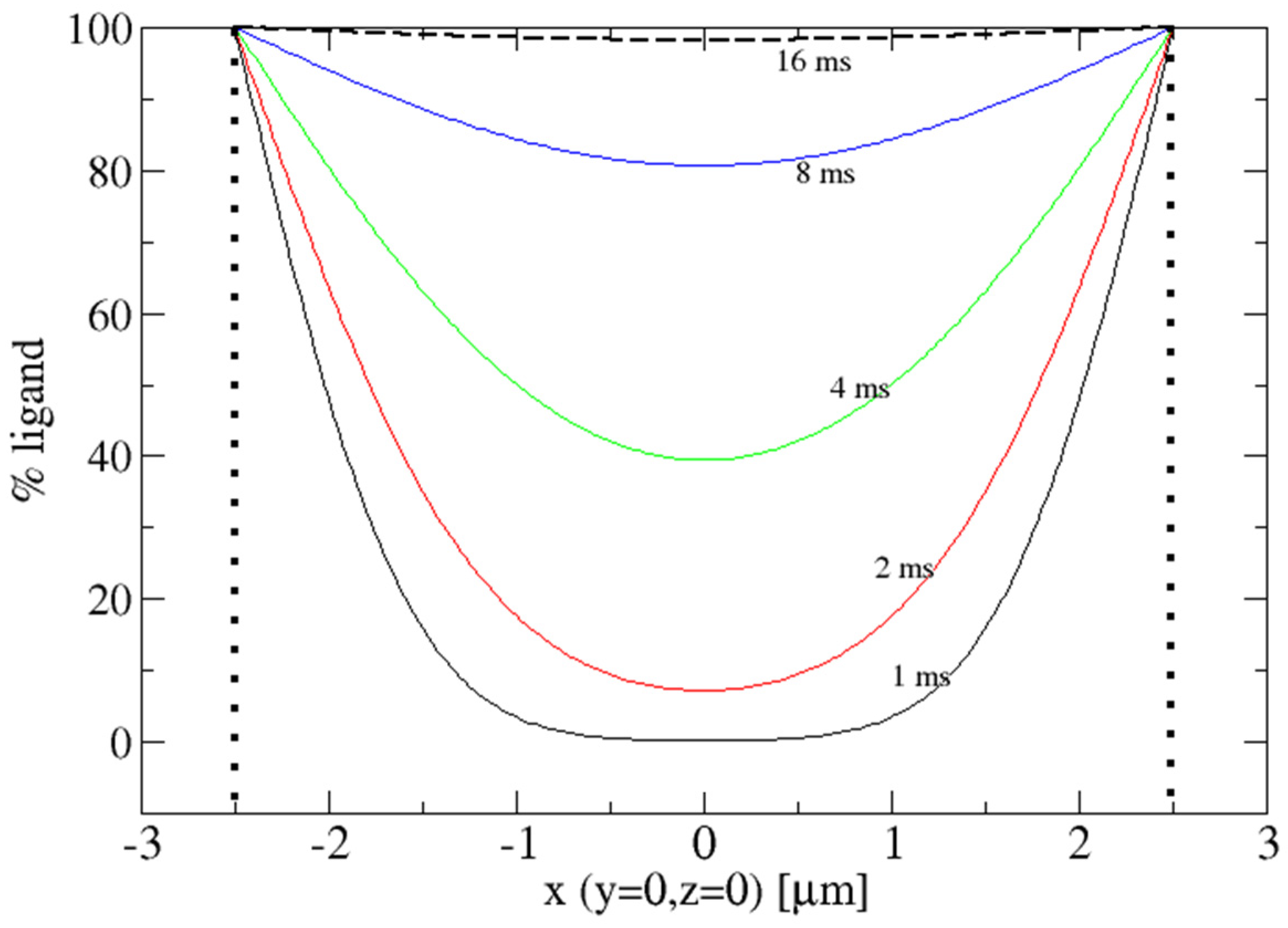



Crystals Free Full Text Reaction Initiation In Enzyme Crystals By Diffusion Of Substrate Html




Enzyme




In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2 Co 3 Is Very Slow With About



Chapter 8 Enzymes




Enzyme Conformation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
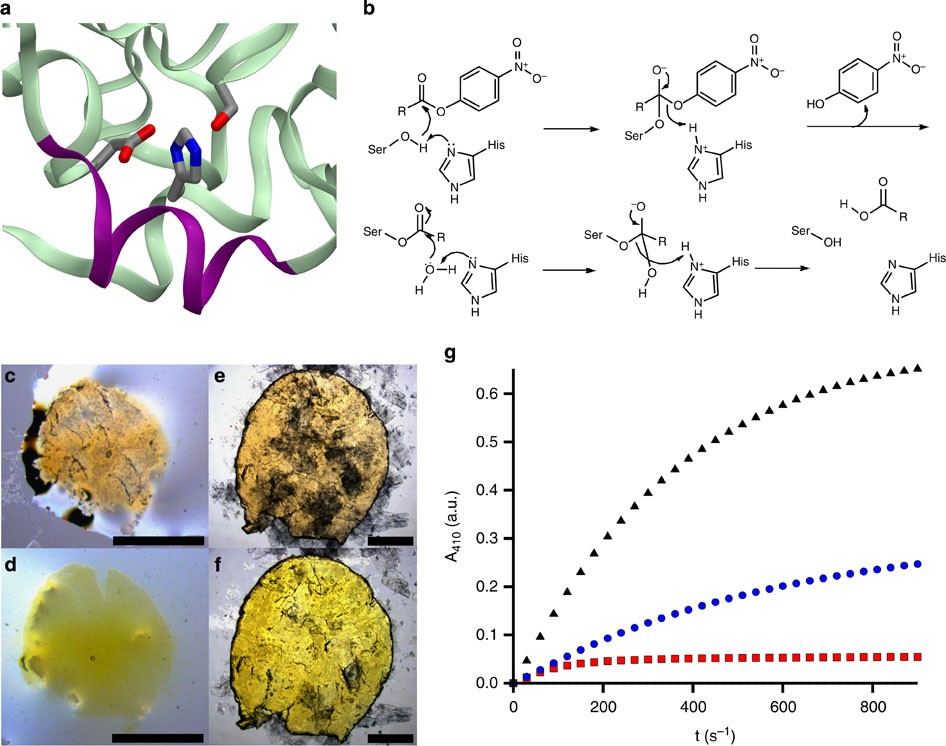



Enzyme Activity In Liquid Lipase Melts As A Step Towards Solvent Free Biology At 150 C Nature Communications




Enzyme Inhibitor Wikipedia
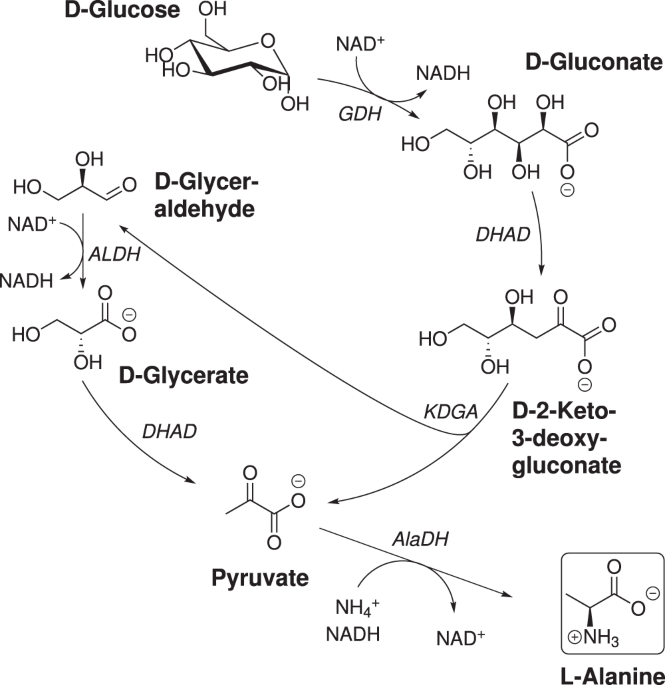



Optimization Of A Reduced Enzymatic Reaction Cascade For The Production Of L Alanine Scientific Reports




3 Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase An Enzyme At The Crossroads Of Sulfane Sulfur Trafficking




Artificial Multienzyme Scaffolds Pursuing In Vitro Substrate Channeling With An Overview Of Current Progress Acs Catalysis
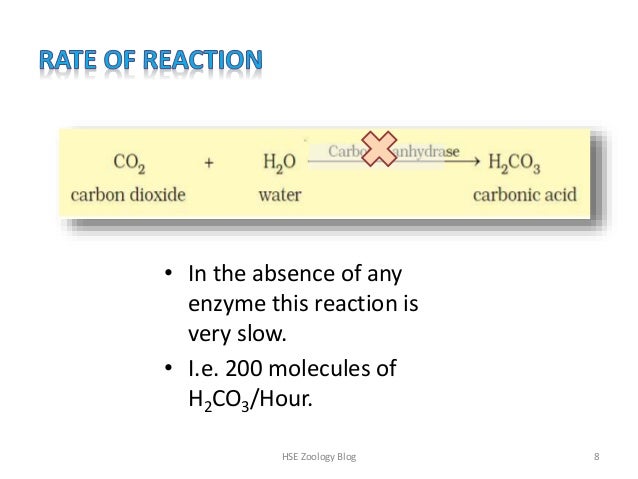



Enzymes
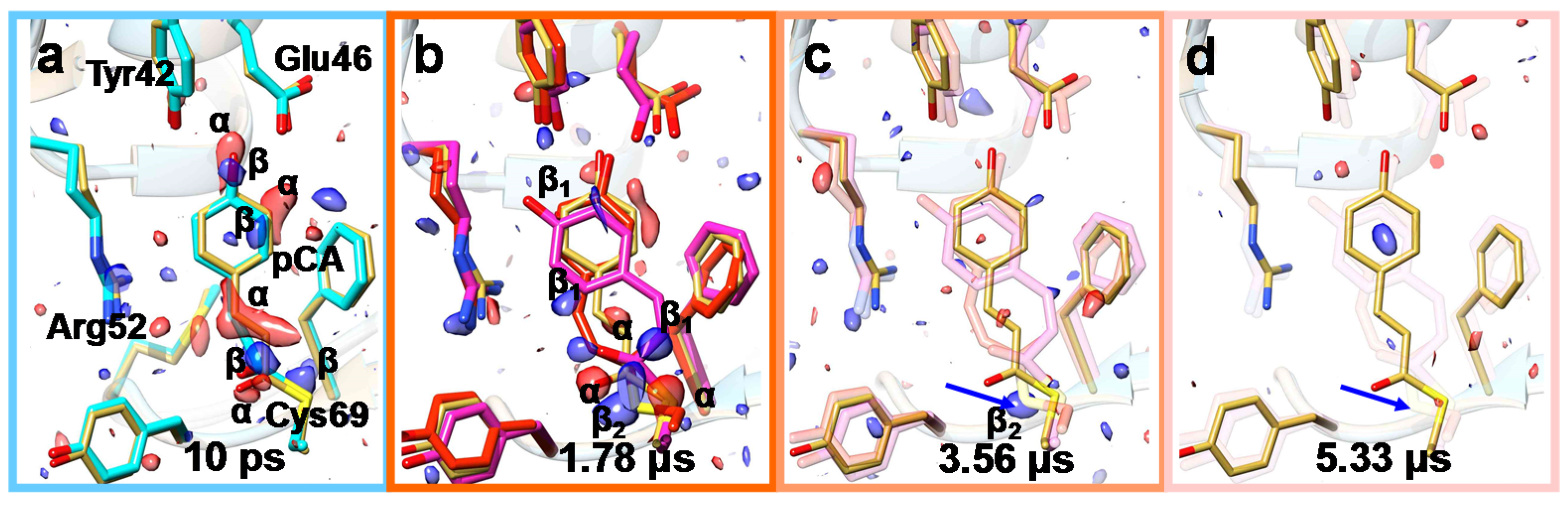



Crystals Free Full Text Reaction Initiation In Enzyme Crystals By Diffusion Of Substrate Html



Chapter 8 Enzymes




Enzyme Synthesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2 Co 3 Is Very Slow With About



Enzyme Inhibitor Wikipedia



Substrate Channelling As An Approach To Cascade Reactions Nature Chemistry
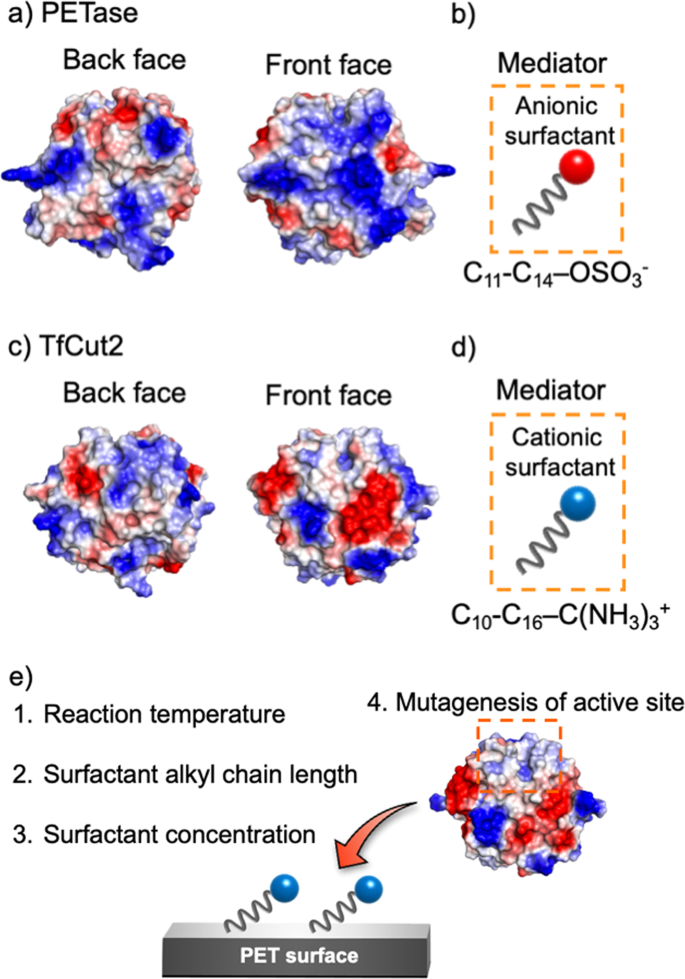



Efficient Degradation Of Poly Ethylene Terephthalate With Thermobifida Fusca Cutinase Exhibiting Improved Catalytic Activity Generated Using Mutagenesis And Additive Based Approaches Scientific Reports




Enzyme Inhibitor Wikipedia
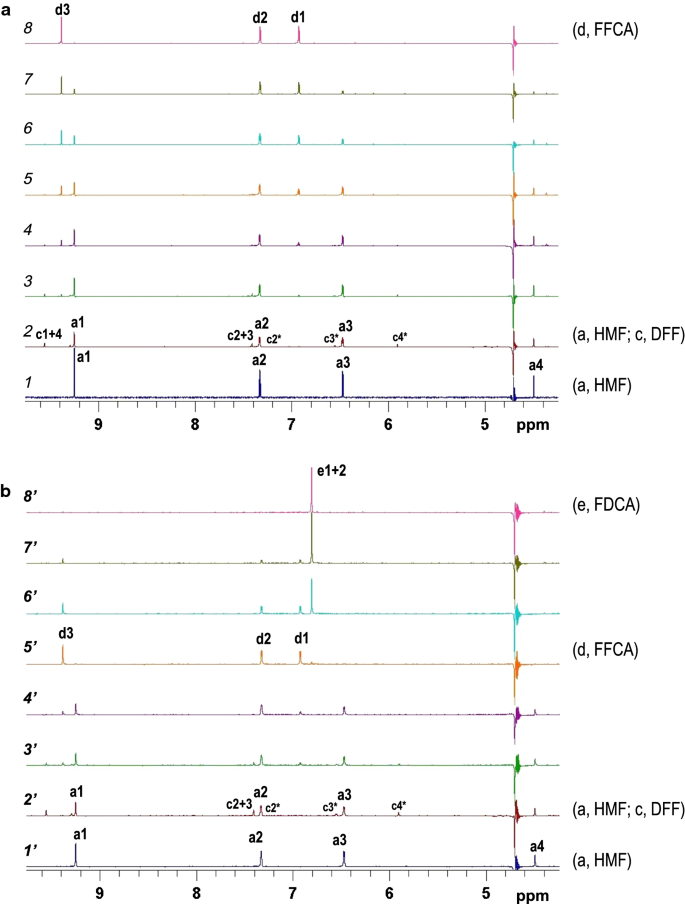



Complete Oxidation Of Hydroxymethylfurfural To Furandicarboxylic Acid By Aryl Alcohol Oxidase Biotechnology For Biofuels Full Text



Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry




Viperin An Ancient Radical Sam Enzyme Finds Its Place In Modern Cellular Metabolism And Innate Immunity Journal Of Biological Chemistry




In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2 Co 3 Is Very Slow With About




Substrate Concentration An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Jstor Org




Enzyme Synthesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
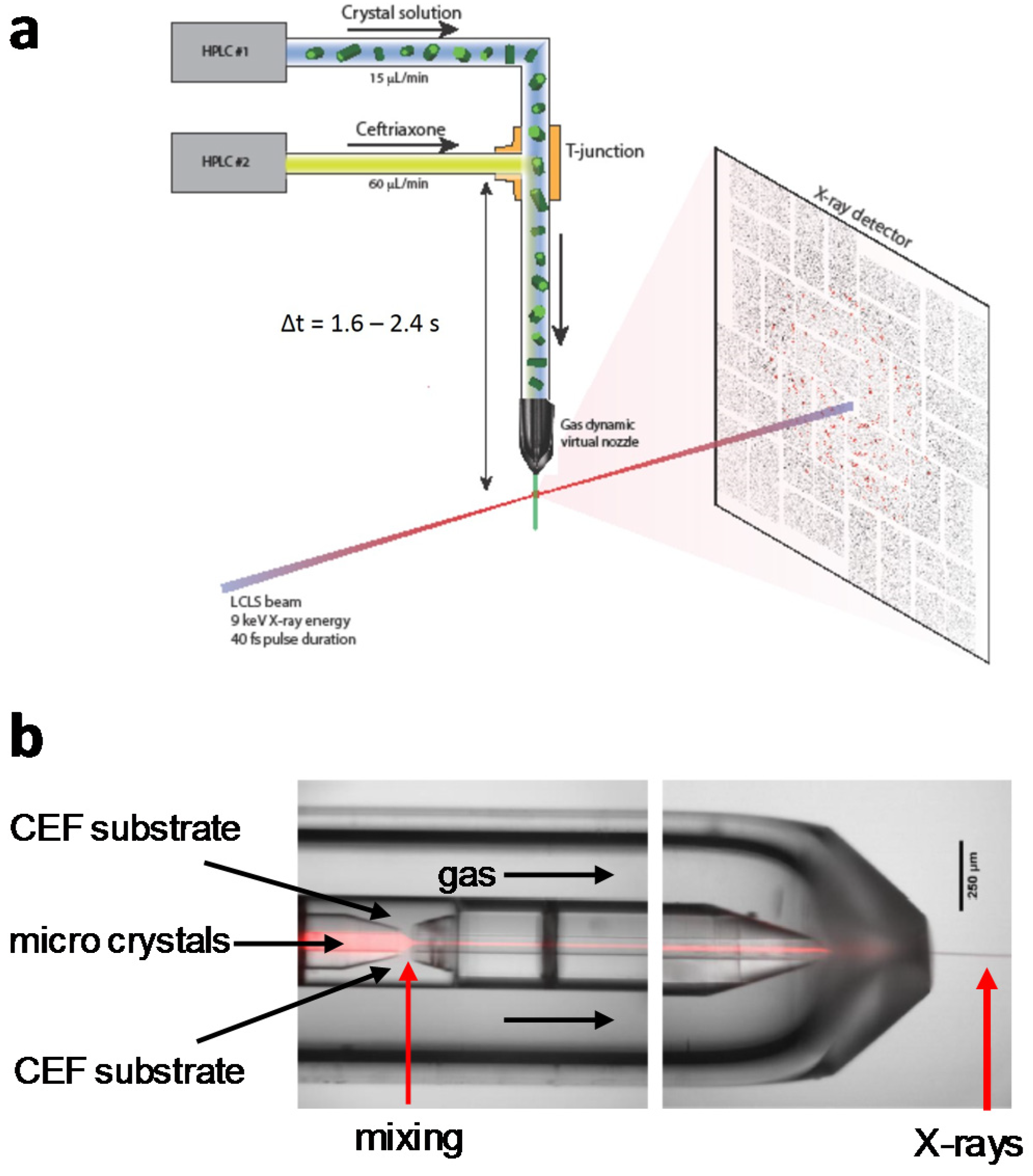



Crystals Free Full Text Reaction Initiation In Enzyme Crystals By Diffusion Of Substrate Html




Rubisco Proton Production Can Drive The Elevation Of Co2 Within Condensates And Carboxysomes Pnas
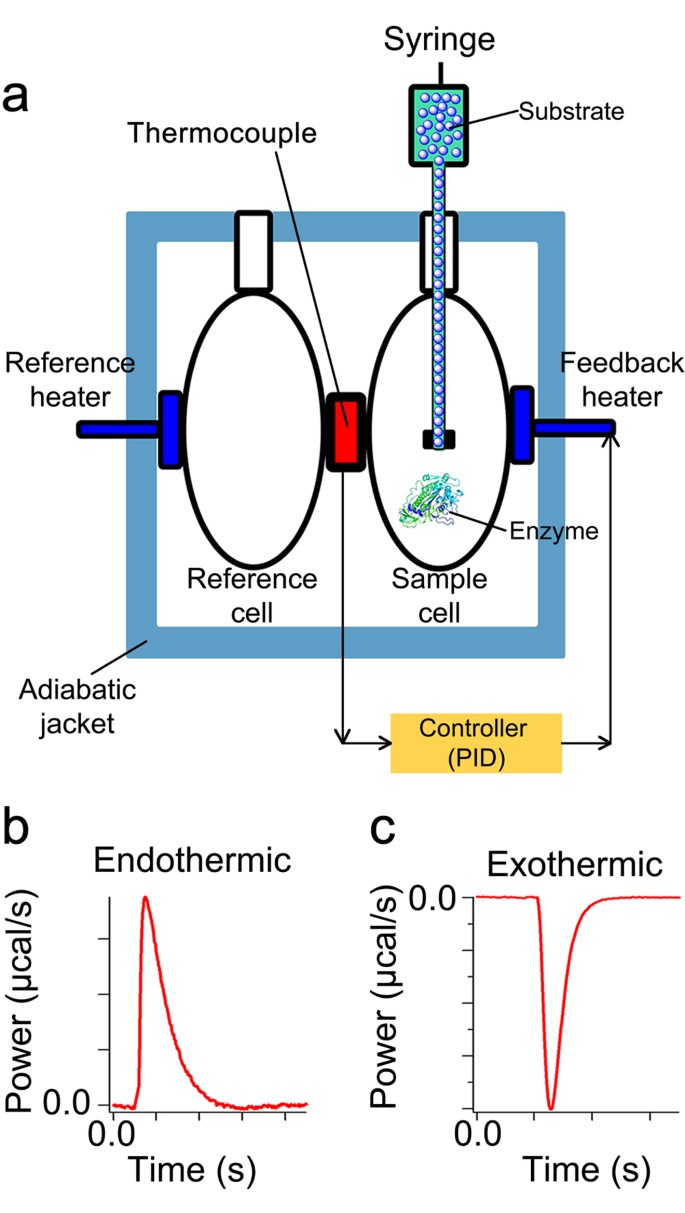



Accurate Label Free Reaction Kinetics Determination Using Initial Rate Heat Measurements Scientific Reports



Pdf Brief Review On Enzyme Activity




Enzyme Synthesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Electrostatic Basis For Enzyme Catalysis Chemical Reviews
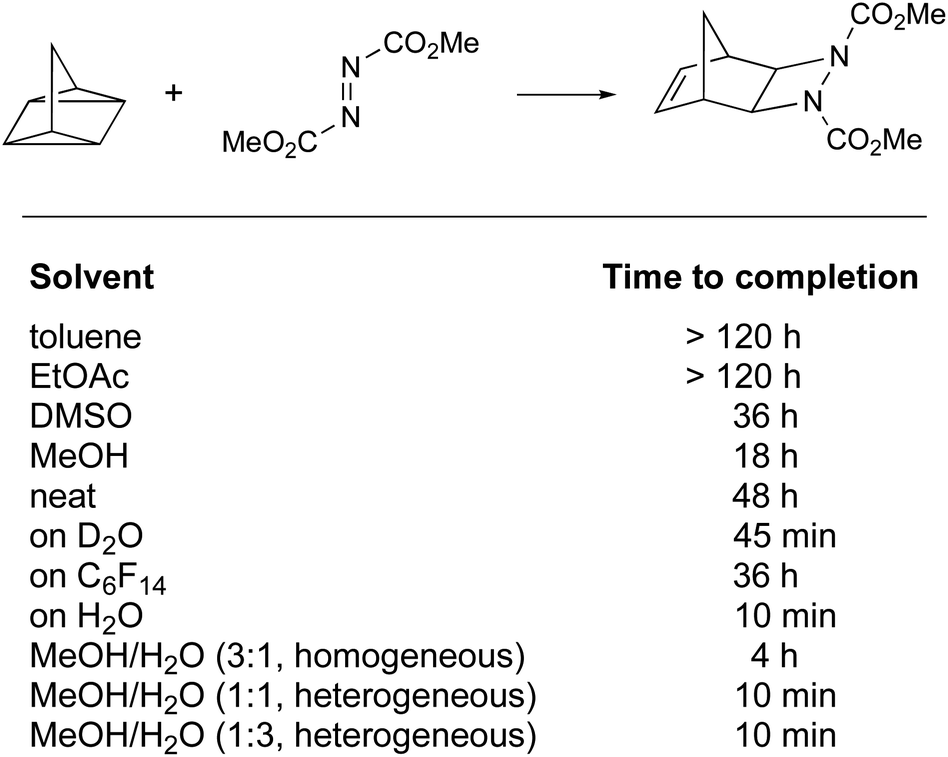



Water As The Reaction Medium In Organic Chemistry From Our Worst Enemy To Our Best Friend Chemical Science Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D0scc
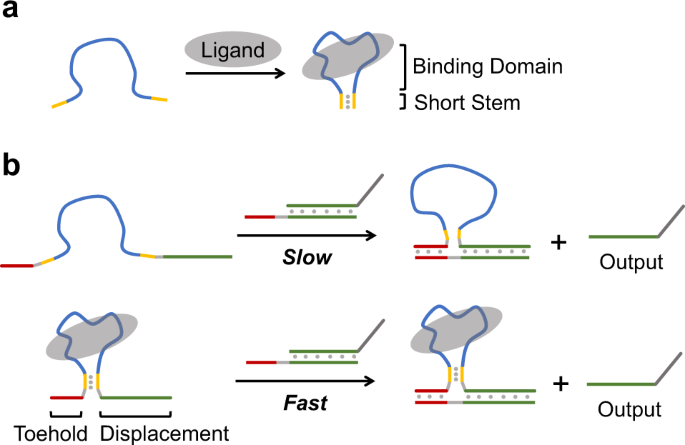



A Kinetically Controlled Platform For Ligand Oligonucleotide Transduction Nature Communications




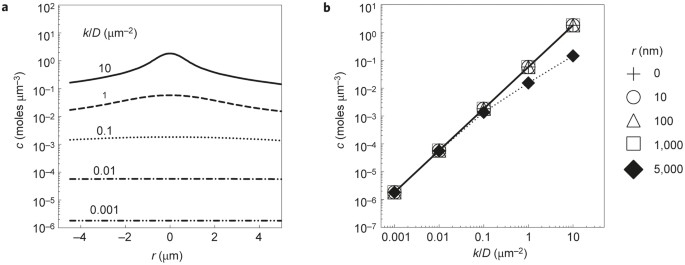
Master Curve Of Boosted Diffusion For 10 Catalytic Enzymes Pnas




Enzyme Inhibitor An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Enzyme Assays Sciencedirect



2
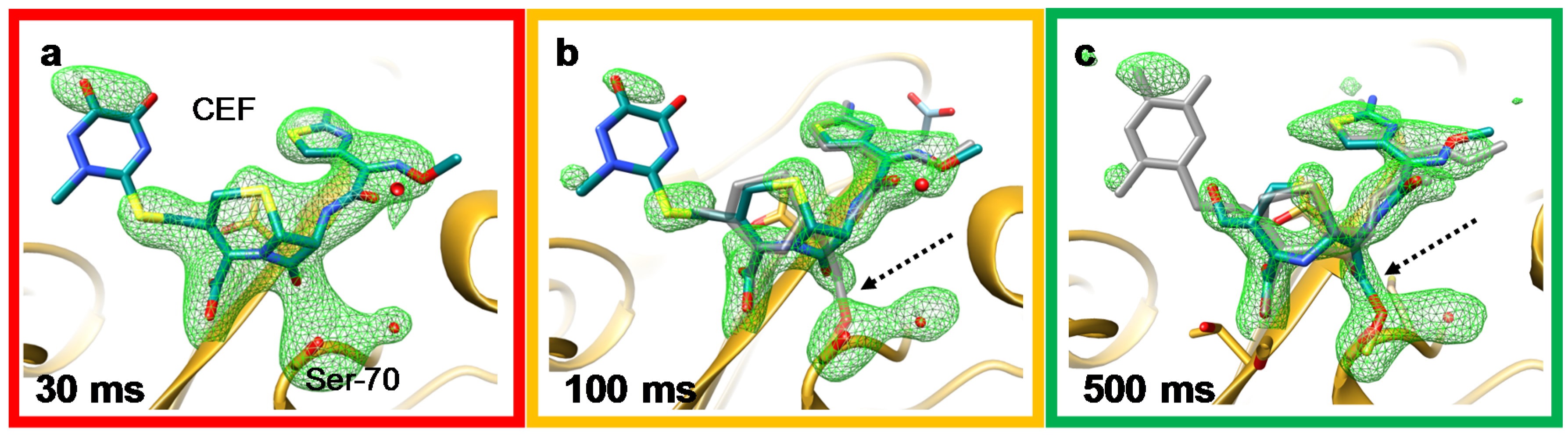



Crystals Free Full Text Reaction Initiation In Enzyme Crystals By Diffusion Of Substrate Html




Study The Reaction Given Below Co 2 H 2 O Underset Enzyme Harr H 2 Co 3 In Absence Of Any Enzyme This Reaction Is Very Slow With 0 Molecules Of H 2 Co 3 Being Formed In An Hour In Presence Of Enzyme



Fruits Gone Bad Discover Enzymatic Browning Scientific American
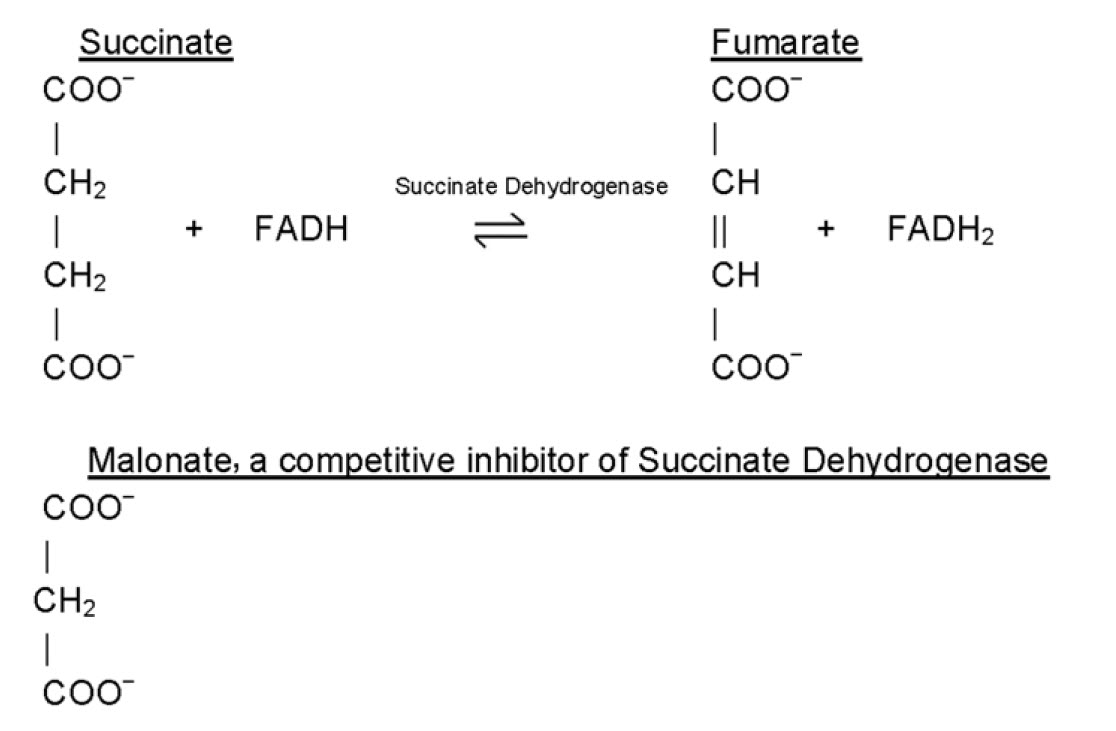



Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry



Enzymes Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Function Human Process System Different Dna




In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2 Co 3 Is Very Slow With About
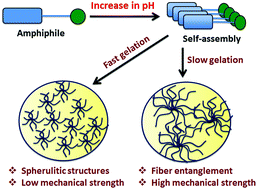



Maintaining Homogeneity During A Sol Gel Transition By An Autocatalytic Enzyme Reaction Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing
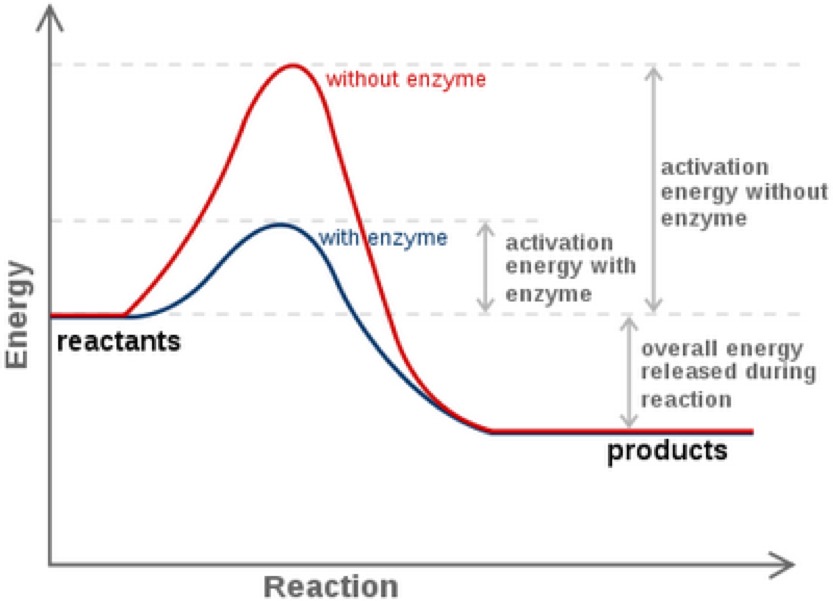



Enzymes And Reaction Rates




Copper Is A Cofactor Of The Formylglycine Generating Enzyme Knop 17 Chembiochem Wiley Online Library




In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2
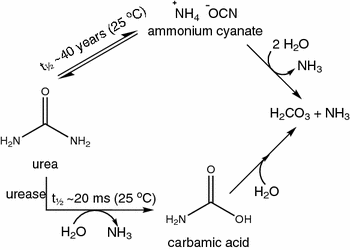



The Molecular Processes Of Urea Hydrolysis In Relation To Ammonia Emissions From Agriculture Springerlink




Dr Hunter Cell Biology Bioenergetics Enzymes And Metabolism




Study The Reaction Given Below Co 2 H 2 O Underset Enzyme Harr H 2 Co 3 In Absence Of Any Enzyme This Reaction Is Very Slow With 0 Molecules Of H 2 Co 3 Being Formed In An Hour In Presence Of Enzyme
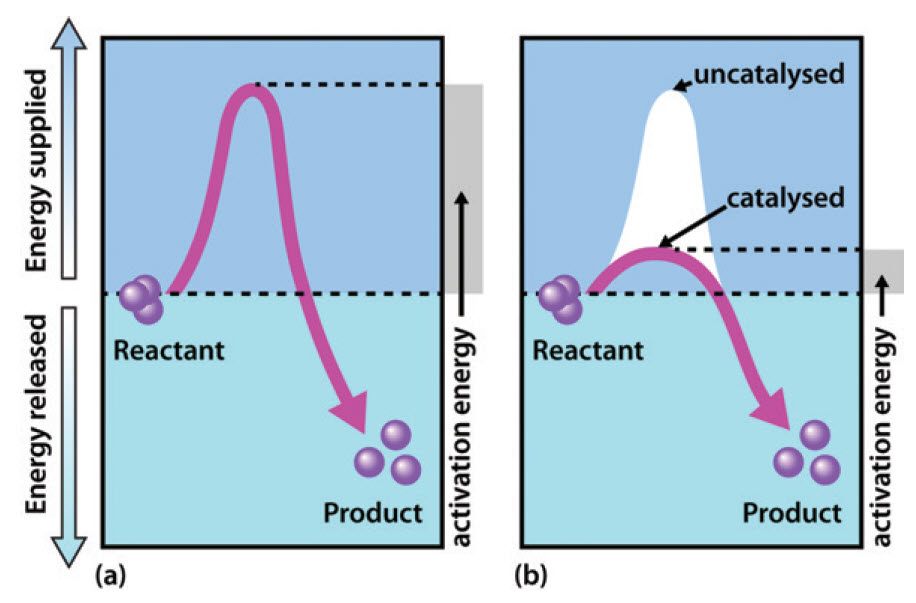



Chapter 6 Enzyme Principles And Biotechnological Applications Chemistry



2




Carbonic Anhydrase Wikipedia




In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2 Co 3 Is Very Slow With About




Proximity Dependent Biotinylation Key Enzymes And Adaptation To Proteomics Approaches Molecular Cellular Proteomics




Looking Back A Short History Of The Discovery Of Enzymes And How They Became Powerful Chemical Tools Heckmann Chemcatchem Wiley Online Library




Looking Back A Short History Of The Discovery Of Enzymes And How They Became Powerful Chemical Tools Heckmann Chemcatchem Wiley Online Library




Pdf Brief Review On Enzyme Activity
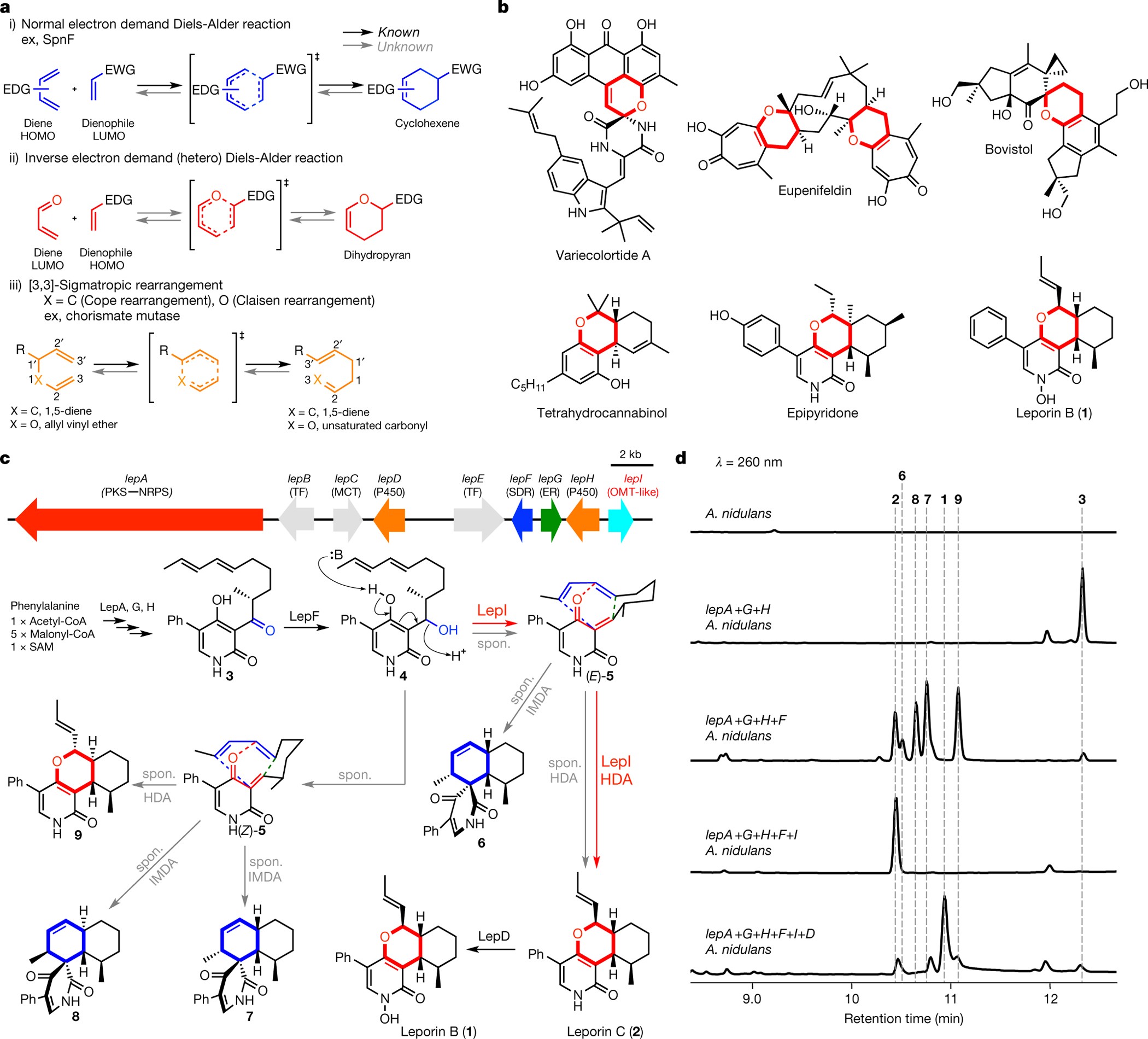



Sam Dependent Enzyme Catalysed Pericyclic Reactions In Natural Product Biosynthesis Nature




Pdf Brief Review On Enzyme Activity




Slow Binding Inhibition A Theoretical And Practical Course For Students Goliĉnik 04 Biochemistry And Molecular Biology Education Wiley Online Library



Energy Enzymes And Catalysis Problem Set




Question In Absence Of Any Enzymes This Reaction Co 2 H 2 O To H 2 Co 3 Is Very Slow With About
コメント
コメントを投稿